Introduction
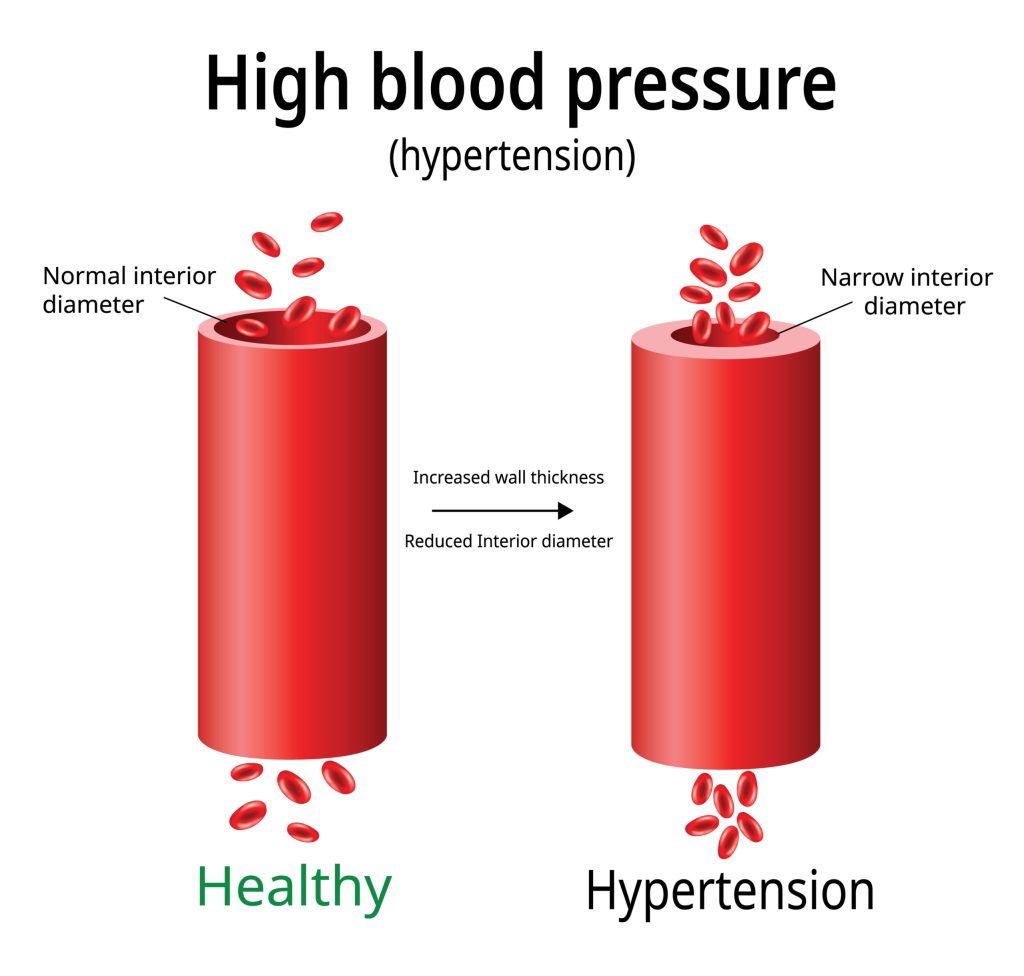
High blood pressure (hypertension) is often called the “silent killer.” Nearly 1.28 billion adults worldwide suffer from it, and many don’t even know their condition—yet it’s a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. The good news? You can effectively manage blood pressure through natural lifestyle shifts, often preventing or reducing the need for medication. In this guide, we’ll explore science-backed tips, practical advice, and daily routines to help you master your blood pressure for life.
1. Understanding Blood Pressure: Numbers That Matter
- What’s Considered Normal?
Healthy readings are typically below 120/80 mmHg. - Why It Matters
High readings strain your heart and arteries, increasing risk for heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage. - When to Act
Stage 1: 130–139 / 80–89 mmHg
Stage 2: ≥ 140 / ≥ 90 mmHg
If readings are consistently elevated, follow a plan right away.
2. Weight: Shedding Pounds, Adding Years of Health
Shedding just 5%–10% of excess body weight can significantly lower blood pressure. For example, dropping 10 pounds could reduce systolic pressure by approximately 5–10 mmHg.
- Track BMI & Waist
Aim for a BMI under 25 or waist circumference under 40″ (men) / 35″ (women). - Use Strategies Like:
- Portion control and mindful eating
- Substituting water for sugary beverages
- Regular exercise routines (20–30 min moderate most days)
3. Eat Smart—Not Just Less
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is a proven model.
- Emphasize: whole fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy, lean protein, legumes
- Avoid: processed foods, excess salt, sugar, saturated fats
Tips to Trust:
- Color your plate—bright fruits and veggies = high potassium
- Swap salt: use herbs like basil, garlic, and spices such as turmeric
- Pre-plan meals to avoid impulse eating
4. Move Your Body
Regular physical activity can lower blood pressure by 4–9 mmHg.
- Best Types: brisk walking, swimming, cycling, tennis
- Goal: at least 150 minutes per week
- Extra Tip:
Integrate mini-workouts—take stairs, walk during calls, or use standing desks.
5. Manage Stress—Your Blood Will Thank You
Stress doesn’t always spike blood pressure chronically, but it plays a key role.
- Try Yoga, meditate, breathe deep
- Practice gratitude, journaling, or nature walks
- Build oasis time into your schedule (even 10 minutes helps)
6. Sleep: The Unsung Hero
Poor sleep raises long-term blood pressure risk. Target 7–9 hours of restful sleep nightly.
- Keep your room dark, cool, gadget-free
- Establish a soothing bedtime routine
- Seek help if you suspect conditions like sleep apnea
7. Limit Alcohol & Quit Smoking
- Alcohol: Keep intake moderate—no more than 1 drink/day for women, 2 for men
- Smoking: Immediate pressure spikes from nicotine—quitting lowers your risk significantly
8. Monitor at Home & Get Regular Check-Ins
- Use a reliable home monitor—measure twice daily after resting
- Share results with your doctor; it can alter treatment decisions significantly
9. When Bad Habits Sneak In: Overcoming Setbacks
- Stay consistent—even small missteps happen
- Build non-food rewards (like self-care or leisure time)
- Lean on support systems—friends, health groups, or professionals
10. Key Takeaways: Sustainable, Smart, Simple
| Strategy | Impact on BP |
|---|---|
| Weight loss | Reduces 5–10 mmHg |
| Healthy eating | Supports 8–14 mmHg |
| Regular movement | Lowers 4–9 mmHg |
| Stress reduction | Supports balance |
| Better sleep | Improves bedtime pressure |
| Limit alcohol/smoking | Immediate health gains |
Set SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, Time-bound.
Related Links & Resources
- American Heart Association – Trusted info on BP management
- Mayo Clinic on DASH Diet – How to implement it at home
- Sleep hygiene tips CDC
- Home BP monitoring guide from AAFP
- Meditation with Headspace (affiliate)